Webhooks
Automate workflows by triggering HTTP requests when content changes in Cockpit.
- Overview
- Features
- Use Cases
- Static Site Deployment
- Notifications
- Search Index Updates
- Data Synchronization
- Audit Logging
- Configuration
- Basic Setup
- Webhook Settings
- Using Environment Variables
- Best Practices
- Security
- Performance
- Reliability
- Testing
Overview
The Webhooks addon enables real-time communication between Cockpit and external services by automatically sending HTTP requests when specific events occur. This is essential for automating workflows, triggering deployments, syncing data, and integrating with third-party services.
Features
- Event-driven triggers - Fire webhooks when content is created, updated, or deleted
- Custom payloads - Send the event data or define your own payload structure
- Custom headers - Add authentication tokens and custom headers
- Multiple HTTP methods - Support for GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
- Environment variables - Use
.envvariables in URLs and headers - Async execution - Webhooks run after the request completes (non-blocking)
- Worker queue support - Offload webhook execution to background workers
- Logging - Failed webhooks are logged for debugging
Use Cases
Static Site Deployment
Trigger Netlify, Vercel, or other static site rebuilds when content changes.
Notifications
Send Slack or Discord notifications when content is published.
Search Index Updates
Keep Algolia, Elasticsearch, or other search indices synchronized.
Data Synchronization
Push content changes to external systems, databases, or CDNs.
Audit Logging
Track content changes in external audit systems.
Configuration
Basic Setup
Navigate to Settings > Webhooks to create and manage webhooks.
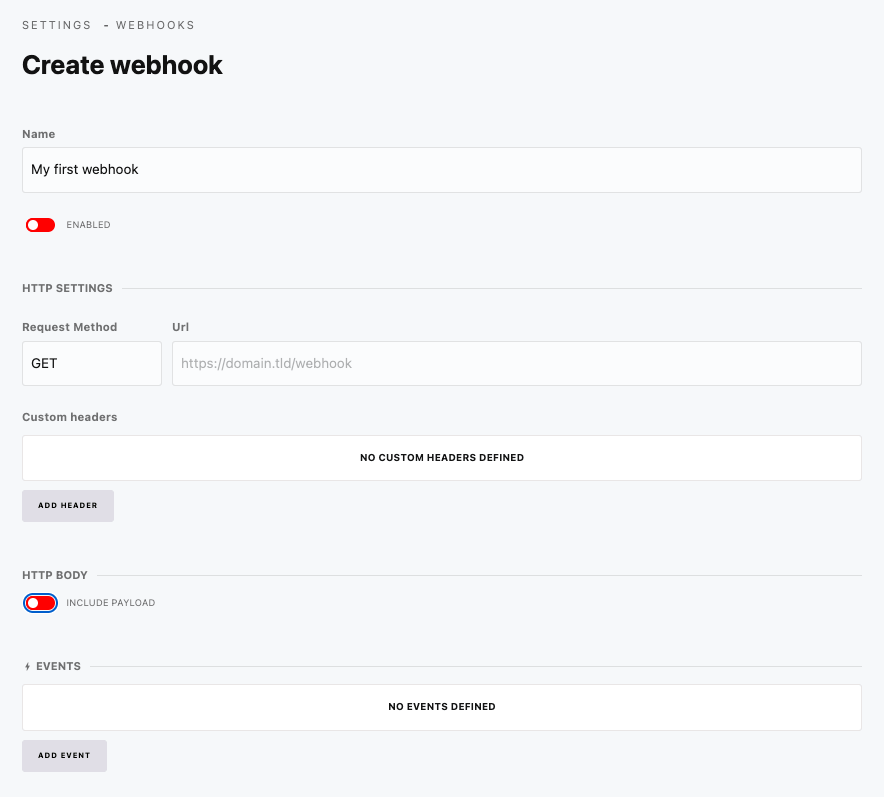
Webhook Settings
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Descriptive name for the webhook |
| URL | The endpoint to call (supports env variables) |
| Method | HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE) |
| Events | Which events trigger this webhook |
| Headers | Custom HTTP headers |
| Payload | Send event data or custom payload |
| Enabled | Toggle webhook on/off |
Using Environment Variables
Use environment variables in URLs and headers for security:
// .env file
DEPLOY_WEBHOOK_URL=https://api.netlify.com/build_hooks/abc123
SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL=https://hooks.slack.com/services/xxx/yyy/zzz
API_TOKEN=your-secret-tokenIn the webhook URL field:
${DEPLOY_WEBHOOK_URL}In headers:
Authorization: Bearer ${API_TOKEN}Best Practices
Security
- Store sensitive URLs and tokens in
.envfiles - Use HTTPS endpoints only
- Implement webhook signature verification on receiving end
- Limit webhook events to what's needed
Performance
- Enable worker mode for high-traffic sites
- Use specific events (e.g.,
content.item.save.posts) instead of broad ones - Keep custom payloads minimal
Reliability
- Implement retry logic on the receiving end
- Monitor webhook logs regularly
- Test webhooks with tools like webhook.site before production use
Testing
Use services like webhook.site to inspect payloads:
- Get a temporary URL from webhook.site
- Set it as your webhook URL
- Trigger the event in Cockpit
- Inspect the received payload
